STIs have a profound impact on sexual and reproductive health around the world. More than 1 million treatable STIs are acquired every day. In 2020, WHO estimated 374 million new infections with 1 of 4 STIs: chlamydia (129 million), gonorrhea (82 million), syphilis (7.1 million) and trichomoniasis (156 million).Most STIs are spread from one person to another through sexual contact through bodily fluids or by skin-to-skin contact by touching an infected part of a person’s body, usually the genitals. Some STIs, such as syphilis, can be spread during childbirth.
Contents
- 1 What is the full name of STD and also give examples?
- 2 (STI) Sexually Transmitted Infection ”venereal disease”
- 3 Symptoms of std
- 4 Lymphogranuloma venereum
- 5 Lymphogranuloma inguinale
- 6 Lesion on penis
- 7 Prevention
- 8 What causes sexually transmitted infections?
- 9 What causes sexually transmitted infections?
- 10 Are sexually transmitted infections contagious?
What is the full name of STD and also give examples?
Venereal diseases or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or sexually transmitted infections are the collective name for diseases caused by sex or intercourse. These are the diseases which can be transmitted in humans or animals through sexual contact. There is a high possibility of the cause spreading.
(STI) Sexually Transmitted Infection ”venereal disease”
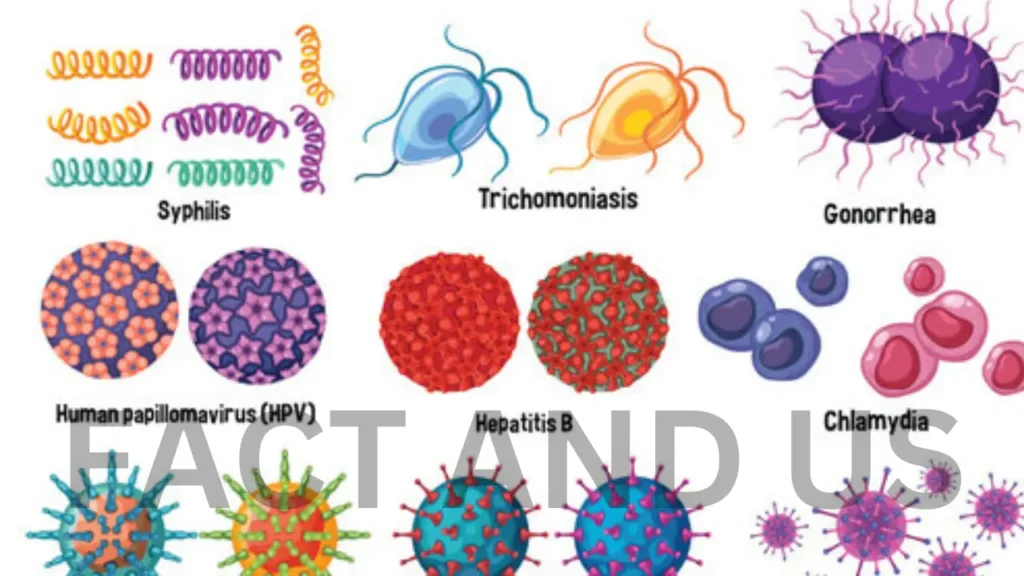
STIs can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. STIs have a devastating impact on adults and infants and affect millions of people each year in the United States. Infection with certain STIs can increase a person’s risk of developing cancer and may increase the likelihood of acquiring or transmitting HIV.Venereal diseases or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or sexually transmitted infections are the collective name for diseases caused by sex or intercourse. These are the diseases which can be transmitted in humans or animals through sexual contact. There is a high possibility of spread due to sexual contact, oral sex, etc. Many times the disease does not show its symptoms in the beginning. This increases the risk of contracting this disease to others. .
More than 30 types of bacteria, viruses and parasites can pass from one person to another through sexual contact. Knowledge about sexually transmitted diseases has been around for hundreds of years. These include (1) Syphilis, (2) Gonorrhoea, (3) Lymphogranuloma Venereum and (4) Chancroid, (5) AIDS.
Symptoms of std
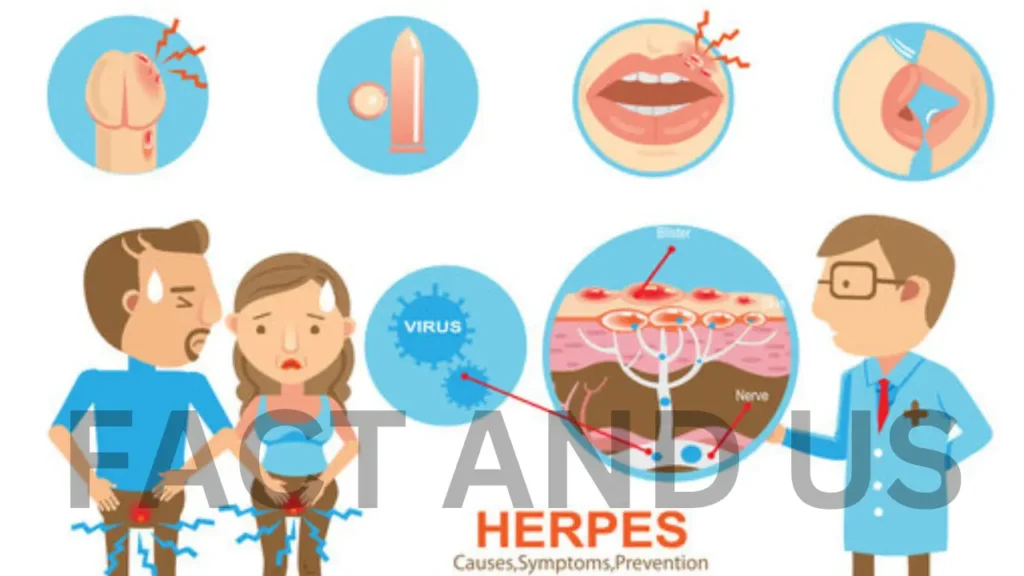
When symptoms of venereal diseases are usually seen in men, they become aware that their sexual organs have been infected. Whereas in women, symptoms of infection are not visible even after the disease has already occurred.
STDs can cause other health problems. Each STD causes different types of health problems overall they can lead to cervical cancer and other cancers, liver disease, infertility, pregnancy problems, and other problems. Some types of STDs increase the chances of HIV/AIDS.
Symptoms of STD include the following –
(1) Itching around the vagina and/or vaginal discharge in women
(2) Discharge from penis in men
(3) Pain during intercourse or urination
(4) Painless red wound around the genitals
(5) Soft skin colored warts appear around the genitals.
(6) Pain in and around the anus for those having anal sex.
(7) Unusual contagious diseases, inexplicable tiredness, night sweats and weight loss.
Lymphogranuloma venereum
A young man suffering from lymphogranuloma venereum has enlarged lymph nodes. Look at both groins.
Inguinal lymph granuloma venereum is a viral infectious disease. In this, there is inflammation in the lymph glands of the genitals and anus. It is transmitted through sexual intercourse and the incubation period is from 3 to 21 days. It starts as a small ulcer, which seems insignificant because it is not painful. Within two to three weeks a lump appears, or the lymph node becomes swollen. The cyst bursts and becomes a ulcer. There are complaints of headache, heat and shivering. Women often suffer from anal inflammation, fever, chills along with shivering, headache and pain in the nodes and later the cysts swell and burst and become ulcers. There is also contraction of the anal canal.
Skin test and complement fixation test are done for diagnosis. Sulfonamides and tetracyclines are used in therapy.
Lymphogranuloma inguinale
In Lymphogranuloma inguinale, granulation tissue increases in the lymph nodes of the thighs. This disease starts on the genitals and reaches both thighs and perineum and becomes a red ulcer. Whether its causative agents are protozoa, or bacteria is still doubtful.
Lesion on penis
Venereal sores: This basically arises from not maintaining cleanliness of the genitals. It appears as a rash on the genitals within 2 to 14 days of sexual intercourse and gradually develops into an ulcer. Lumps form in the lymph glands of the thigh. This ulcer is soft. Treatment is done with sulfonamides.
Prevention
To prevent venereal disease, use of rubber membranes during sex and cleaning the genitals with soap after sex are the best measures. Testing and treatment of venereal diseases should be easily accessible to all and proper information should be given to the general public regarding these diseases, so that people suffering from venereal diseases can give up fear, shyness, hesitation etc. and seek medical advice.
You can protect yourself from STD–
(1) To maintain a marriage relationship yourself and to ensure that your partner also maintains it.
(2) The use of latex condoms by men reduces the fear of contagion if used properly. Keep in mind, always use it during sex. Women’s condoms are not as effective as men’s. If a man does not use them, a woman must do so.
Symptoms and causes
What are the symptoms of sexually transmitted infection?
Symptoms of sexually transmitted infections (STDs) vary depending on the type. You may not have any symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may appear around your genital area and may include:
Lumps, sores, or warts on or around your penis, vagina, mouth, or anus.
Swelling or severe itching near your penis or vagina.
Discharge from your penis.
Vaginal discharge that smells bad, causes burning, or is different in color or quantity from normal.
Vaginal bleeding that is not your period.
Painful sex.
Pain while urinating or frequent urination.
Additionally, you may also have symptoms throughout your body, including:
Red rashes on the skin.
Weight loss.
Diarrhea .
night sweats .
Aches, pains, fever and chills.
Jaundice (yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes).
What causes sexually transmitted infections?
Sexually transmitted infections develop when various bacteria, viruses or parasites infect your body. You can get these microorganisms from bodily fluids (such as blood, urine, semen, saliva and other mucus-lined areas) during sex usually during vaginal, oral and anal sex or other sexual activities.
What causes sexually transmitted infections?
Sexually transmitted infections develop when various bacteria, viruses or parasites infect your body. You can get these microorganisms from bodily fluids (such as blood, urine, semen, saliva and other mucus-lined areas) during sex usually during vaginal, oral and anal sex or other sexual activities.
Are sexually transmitted infections contagious?
Yes, sexually transmitted infections (STDs) are contagious. Most STIs are spread from person to person through sexual contact through bodily fluids or by skin-to-skin contact by touching an infected part of a person’s body, usually the genitals. Some STIs, such as syphilis, can be spread during childbirth.
If you have an STI, it is important to see a healthcare provider to receive treatment. Some STIs are treatable. If you’re sexually active, you can prevent the spread of STIs by getting tested regularly, talking to your sexual partner about your diagnosis, and using protection during sex.
Stay connected with Fact and US for more such news.
