Contents
Eye Disease
Researchers from King’s, with doctors at King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, have successfully used a new robot system to improve treatment for debilitating eye disease. The custom-built robot was used to treat wet neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD), administering a one-off, minimally invasive dose of radiation, followed by patients’ routine treatment with injections into their eye. In the landmark trial, published today in The Lancet, it was found that patients then needed fewer injections to effectively control the disease, potentially saving around 1.8 million injections per year around the world.

Wet AMD is a debilitating eye disease where abnormal new blood vessels grow into the macula, the light-sensing layer of cells inside the back of the eyeball. The vessels then start to leak blood and fluid, typically causing a rapid, permanent, and severe loss of sight. Globally, around 196 million people have AMD, and the Royal College of Ophthalmologists estimates that the disease affects more than 70,000 people in the UK. The number of people with AMD is expected to increase 60% by 2035, due to the country’s ageing population.
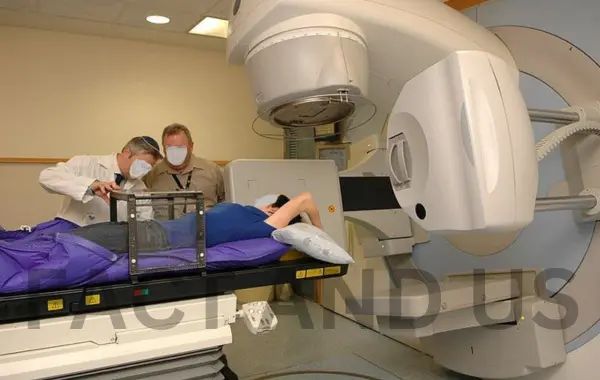
Wet AMD is currently treated with regular injections into the eye. Initially, treatment substantially improves a patient’s vision. But, because the injections don’t cure the disease, fluid will eventually start to build up again in the macula, and patients will require long-term, repeated injections. Most people require an injection around every 1-3 months, and eye injections, costing between $500 and $800 per injection, have become one of the most common NHS procedures. The new treatment can be targeted far better than existing methods, aiming three beams of highly focused radiation into the diseased eye. Scientists found that patients having robotic radiotherapy required fewer injections to control their disease compared to standard treatment. The study found that the robotically controlled device saves the NHS $565 for each patient treated over the first two years, as it results in fewer injections.
Journal Reference:
Timothy L Jackson, Riti Desai, Hatem A Wafa, Yanzhong Wang, Janet Peacock, Tunde Peto, Usha Chakravarthy, Helen Dakin, Sarah Wordsworth, Cornelius Lewis, Patricia Clinch, Lisa Ramazzotto, James E Neffendorf, Chan Ning Lee, Joe M O’Sullivan, Barnaby C Reeves, Salwa Abugreen, Mandeep Bindra, Ben Burton, Indra Dias, Christiana Dinah, Ravikiran Gandhewar, Athanasios Georgas, Srinivas Goverdhan, Ansari Gulrez, Richard Haynes, Edward Hughes, Timothy Jackson (Chief Investigator), Afsar Jafree, Sobha Joseph, Tarek Kashab, Luke Membrey, Geeta Menon, Aseema Misra, Niro Narendran, Douglas Newman, Jignesh Patel, Sudeshna Patra, Robert Petrarca, Prakash Priya, Arora Rashi, Ramiro Salom, Paritosh Shah, Izadi Shahrnaz, George Sheen, Marianne Shiew, Paul Tesha, Eleni Vrizidou. Stereotactic radiotherapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (STAR): a pivotal, randomised, double-masked, sham-controlled device trial.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Ask your care team about the side effects you might get.
(1)Sore skin
In some people, radiotherapy can make your skin sore, change colour (it might become red, lighter, or darker than your normal skin tone), or dry and itchy. Sometimes it can blister and peel.
(2)Tiredness
Many cases of tiredness are due to stress, not enough sleep, poor diet, and other lifestyle factors. Try these self-help tips to restore your energy levels. If you feel you’re suffering from fatigue, which is an overwhelming tiredness that isn’t relieved by rest and sleep, you may have an underlying medical condition
(3)Hair loss
It can be the result of heredity, hormonal changes, medical conditions, or a normal part of aging. Anyone can lose hair on their head, but it’s more common in men. Baldness typically refers to excessive hair loss from your scalp. Hereditary hair loss with age is the most common cause of baldness.
(4)Feeling sick
A person may always feel nauseous due to a lack of sleep, poor diet, anxiety, or stress. These factors can make a person more susceptible to infection and illness. However, always feeling sick can also signify pregnancy or chronic illness.
(5) Problems eating and drinking
Dysphagia is the medical term for swallowing difficulties. Some people with dysphagia have problems swallowing certain foods or liquids, while others can’t swallow at all. Other signs of dysphagia include coughing or choking when eating or drinking.
(6)Diarrhoea
Diarrhoea is defined as the passage of 3 or more loose or liquid stools per day (or more frequent passage than is normal for the individual). Frequent passing of formed stools is not diarrhoea, nor is the passing of loose, pasty stools by breastfed babies.
(7) Stiff joints and muscles
Stiff joints can be caused or made worse by a number of factors. Not all joint stiffness is caused by aging. The stiffness can be a sign of an underlying condition. Conditions that cause joint stiffness include arthritis, gout, bursitis, lupus, bone cancer, and degenerative joint disease in Atlanta.
(8)Sex and fertility issues
Sexual problems that interfere with intercourse and prevent conception can have a deep impact on couples. Problems in any of the phases of sexual response (desire, arousal, orgasm, resolution) as well as pain disorders may contribute to infertility.
Which radiation is used in eye treatment?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays to kill cancer cells. It is a common treatment for eye melanoma.
Designing Environments That Are Robot-Inclusive
May 31, 2024 To overcome issues associated with real-life testing, researchers successfully demonstrated the use of digital twin technology within robot simulation software in assessing a robot’s suitability for…
What are 3 types of radiation used in radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves, such as x-rays, gamma rays, electron beams, or protons, to destroy or damage cancer cells.
Robot ANYmal Can Do Parkour and Walk Across Rubble
Mar. 13, 2024 The quadrupedal robot ANYMA went back to school and has learned a lot. Researchers used machine learning to teach it new skills: the robot can now climb over obstacles and successfully negotiate…
Glaucoma Could Be Successfully Treated With Gene Therapy
Apr. 21, 2020 A new study has shown a common eye condition, glaucoma, could be successfully treated with a single injection using gene therapy, which would improve treatment options, effectiveness and quality of…
Which radiation therapy is best?
External beam radiation therapy is used to treat many types of cancer. Brachytherapy is most often used to treat cancers of the head and neck, breast, cervix, prostate, and eye. A systemic radiation therapy called radioactive iodine, or I-131, is most often used to treat certain types of thyroid cancer
Is radiation harmful to eyes?
How Radiation Affects Eyes: Know the Risks & Prevention
The eye is a delicate organ that includes a network of tissues and cells and is vulnerable to the harmful effects of radiation. Exposure to ionizing radiation can damage the cells of the cornea, lens, and retina, leading to a range of eye conditions
Optical Imager Poised to Improve Diagnosis and Treatment of Dry Eye Disease
Oct. 4, 2019 Researchers have developed a new non-invasive optical imaging system that promises to improve diagnosis and treatments for dry eye disease. Dry eye, which often causes irritation and blurred vision,
Is eye radiation painful?
Although you might have some pain after surgery, you do not feel the radiation from the plaque. Usually you have a gauze pad and a protective shield over the eye being treated. These stay over your eye while the plaque is in place. Your nurse will check your eye regularly for signs of inflammation or infection.
Side effects-Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy can cause side effects, although many of these can be treated or prevented, and most will go away after the treatment stops. It’s difficult to predict what side effects you’ll get, and in some cases you may only develop side effects months, or even years, after you start treatment. Side effects vary from person to person and depend on things such as the part of your body being treated and the type of radiotherapy you have. Ask your care team about the side effects you might get.
Stay connected with FACT AND US for more such news.
